





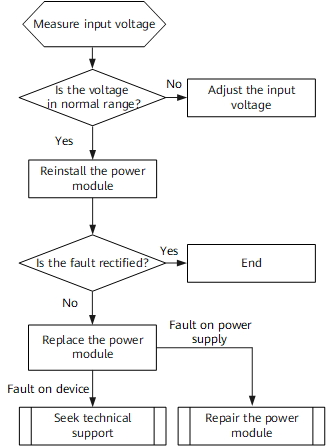














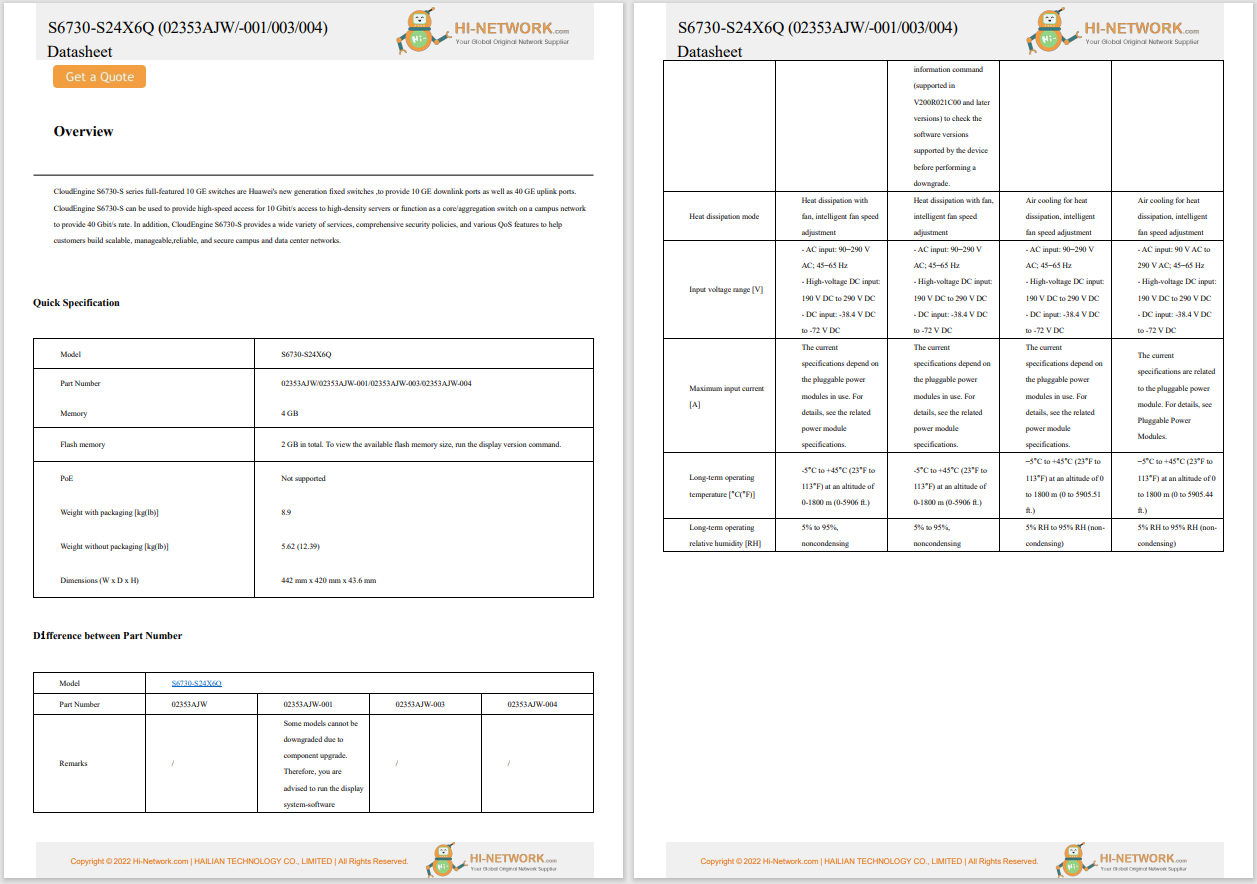
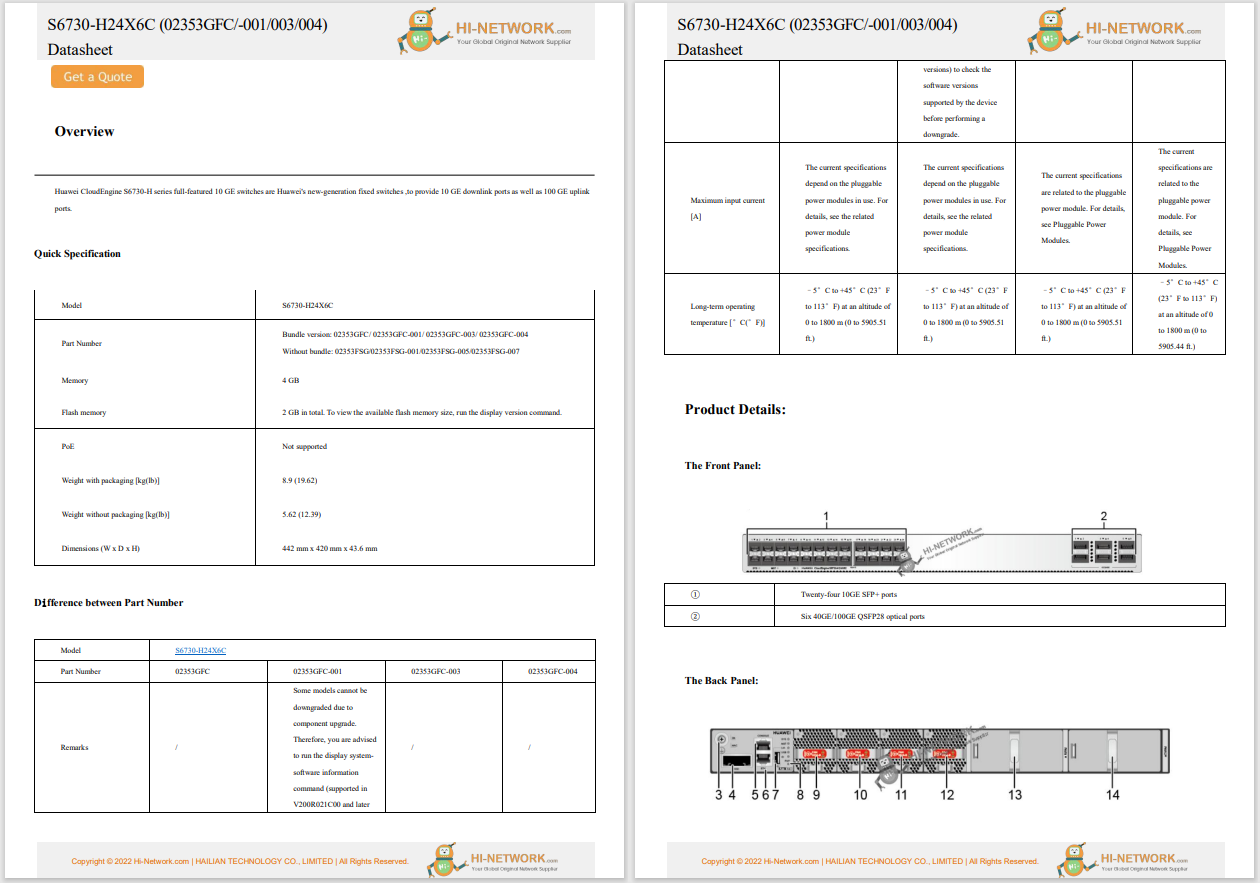

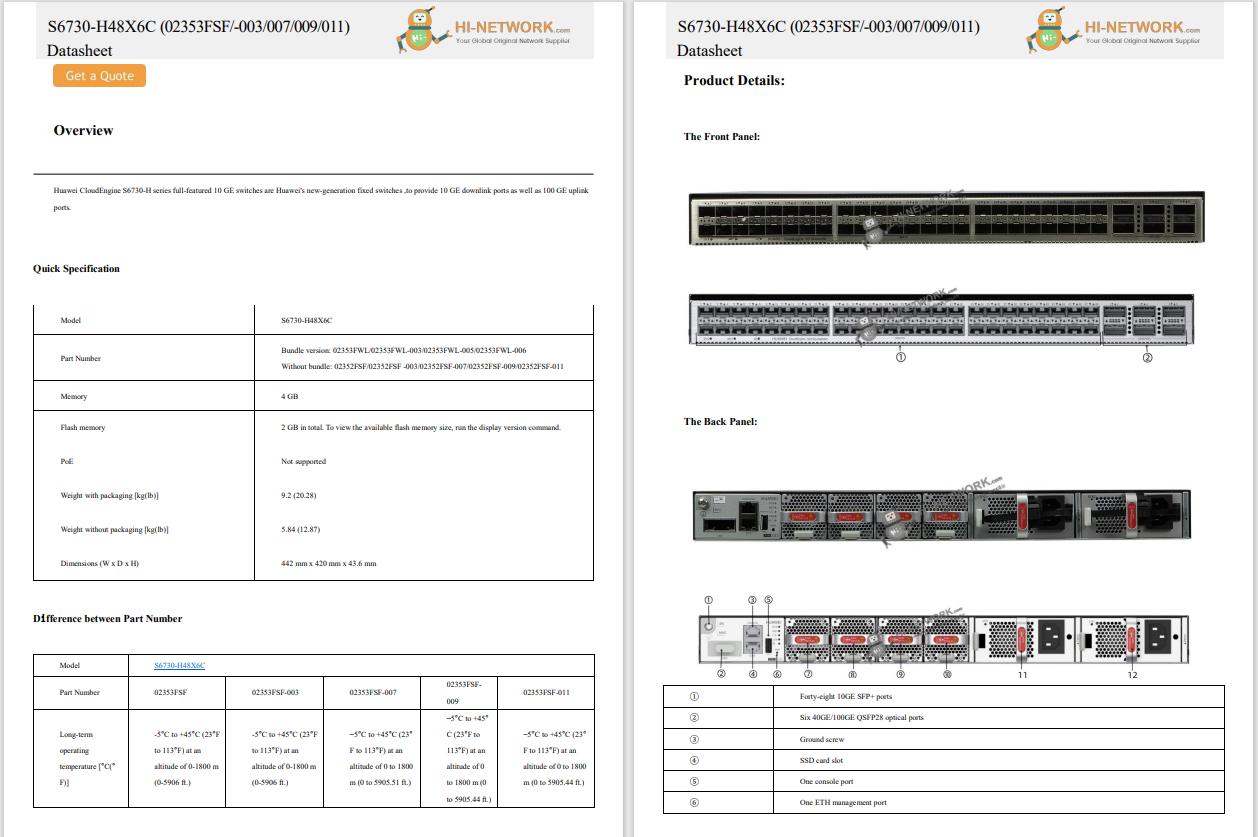




The Lazarus group, a North Korean threat actor, is targeting Windows IIS web servers to conduct espionage attacks, according to a new analysis from the AhnLab Security Emergency Response Center (ASEC).
The attackers use weakly managed or vulnerable web servers as an initial entry point before executing their malicious commands later, according to the researchers, who say the tactic is a variation of the dynamic-link library (DLL) side-loading technique regularly used by the state-affiliated group. The threat actors use the Windows IIS web server process, w3wp.exe, to drop a malicious DLL (msvcr100.dll) in the same folder path as a normal application (Wordconv.exe). They then run the normal application to trigger the malicious DLL to run. After the initial infiltration, Lazarus uses the open-source 'colour picker plugin', a plugin for Notepad++, to gain a foothold before creating additional malware (diagn.dll). This malware, which is ideal for conducting espionage operations, facilitates identity theft and lateral movement.
ASEC highlighted the increasingly sophisticated nature of the Lazarus group and their ability to use a variety of attack vectors to achieve their initial breach. They added that to block the threat group from carrying out activities such as information leakage and lateral movement; organisations should proactively monitor for anomalous process execution relationships and take preventative measures.
 Etiquetas calientes:
ciberseguridad
ciberdelitos
Etiquetas calientes:
ciberseguridad
ciberdelitos