





















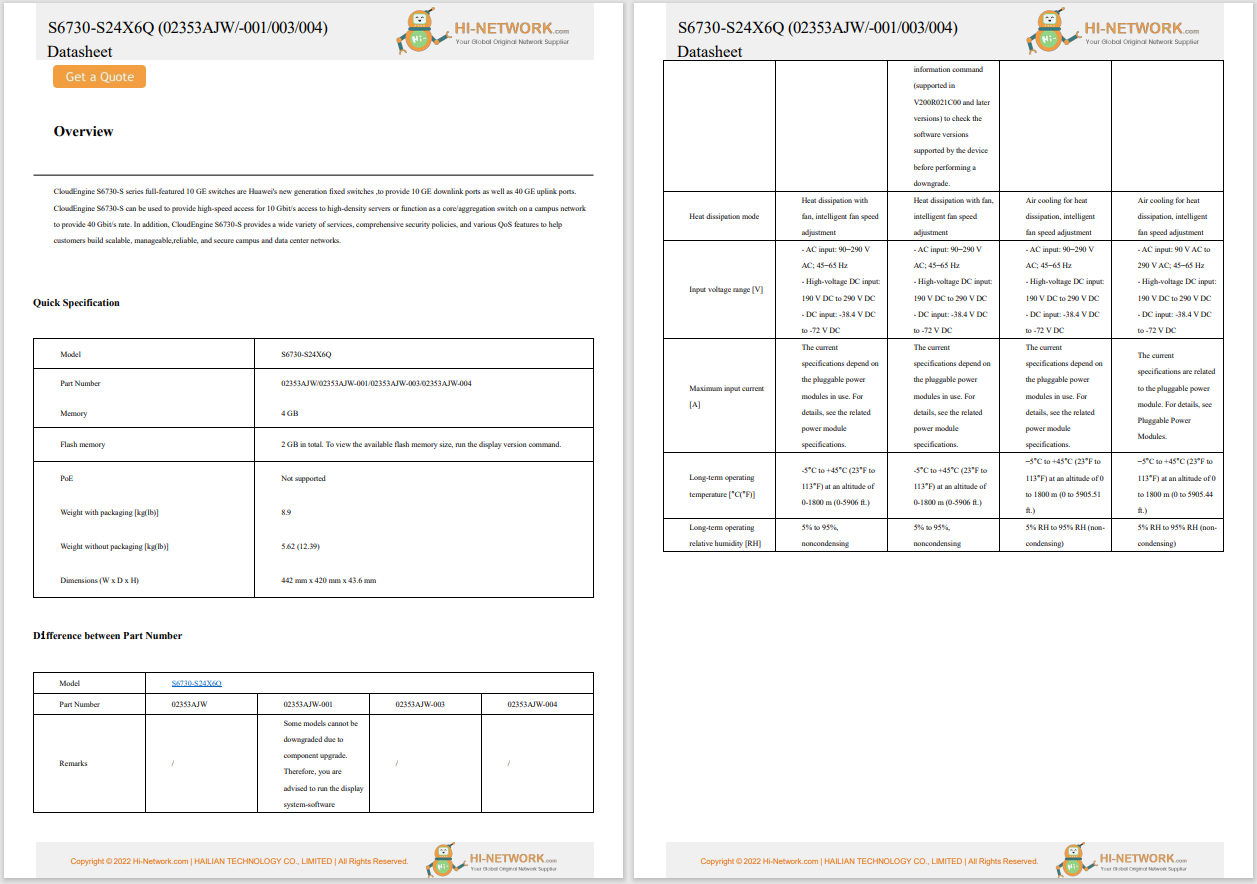
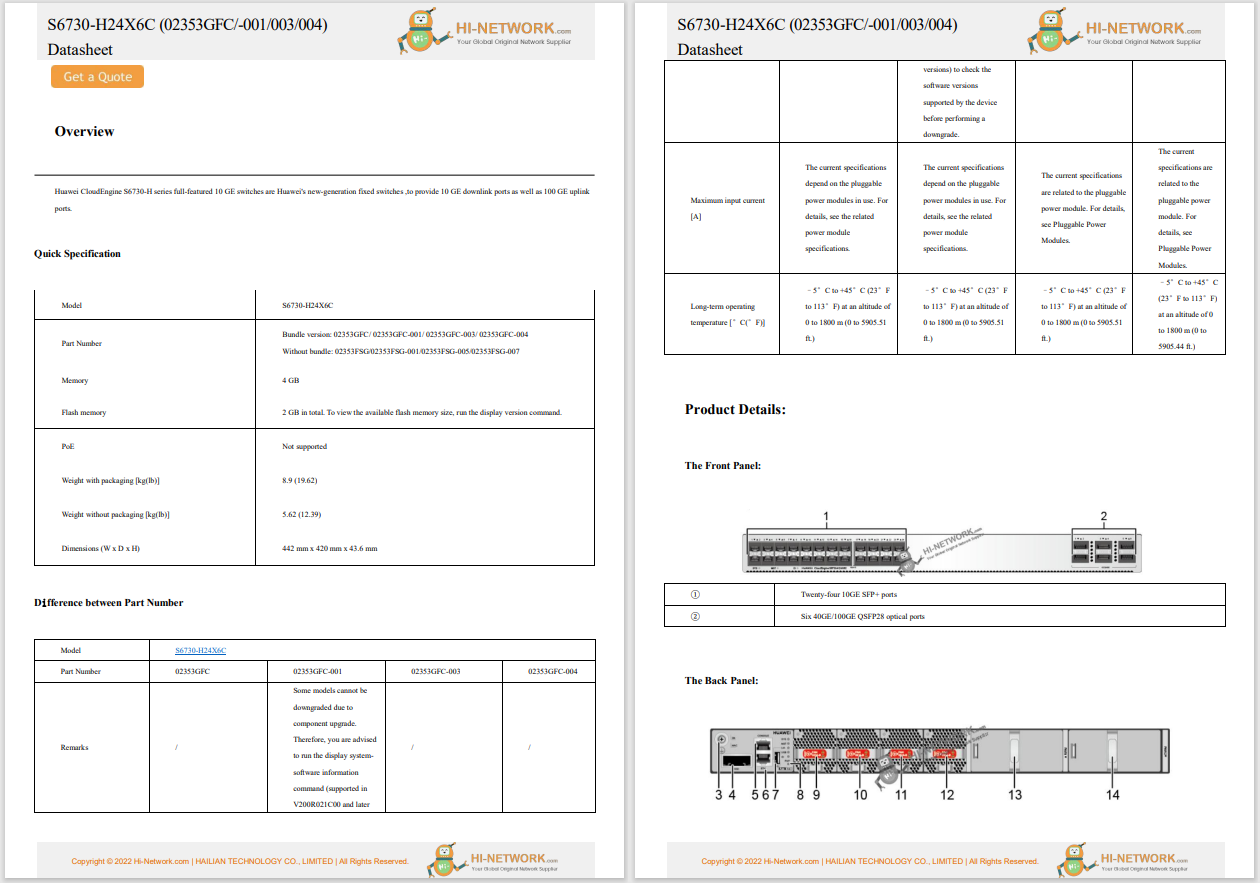

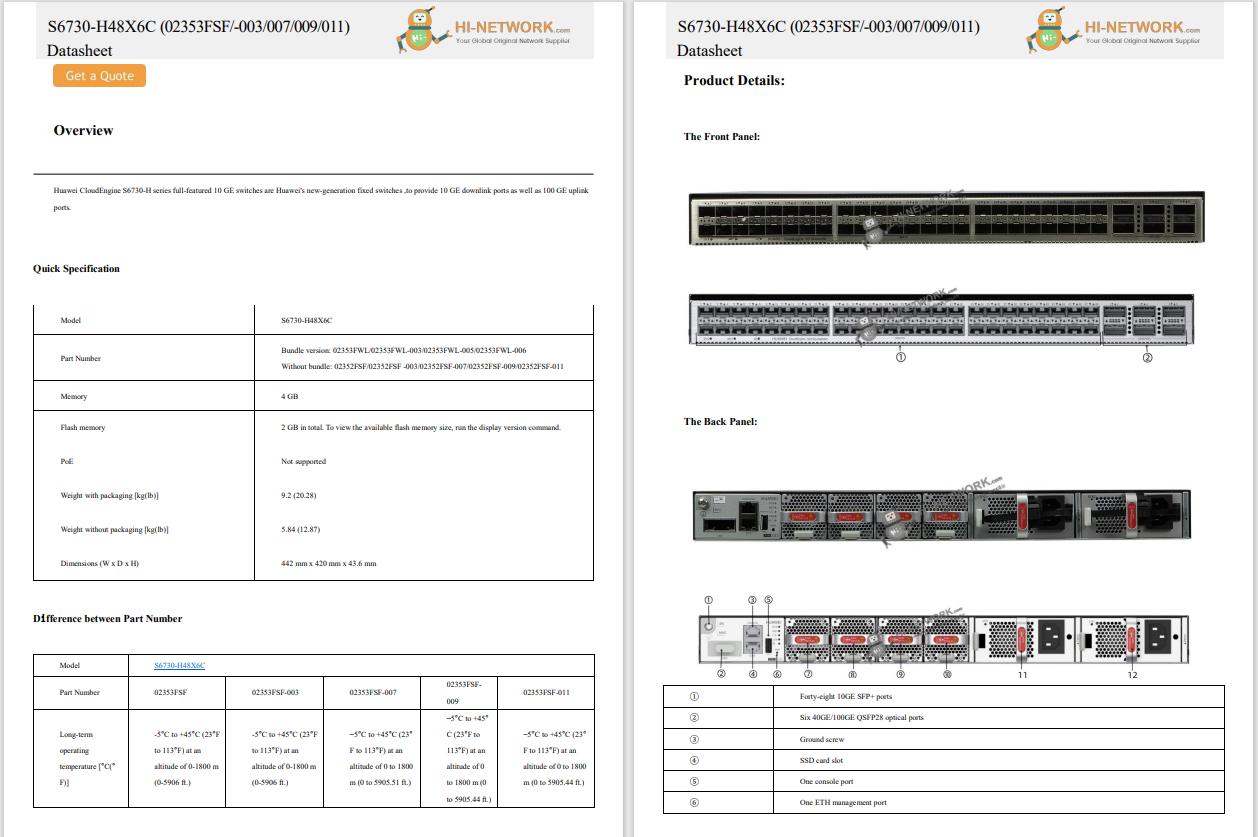


New progress has been made in investigating the cyberattack on the Wuhan Earthquake Monitoring Center, which occurred on 26 July. A joint investigation team formed by the National Computer Virus Emergency Response Center (CVERC) discovered malicious backdoor software with US intelligence characteristics.
The CVERC team found a very complex backdoor malware on the victim's network that has the characteristics of US intelligence services, is highly stealthy, and is designed to steal data related to earthquake monitoring with a clear military reconnaissance objective. Experts characterised it as planned and premeditated cyber military reconnaissance action. Experts also revealed that earthquake monitoring data includes rich geographical and geological data such as surface deformation and hydrological monitoring,
'After many years of continuous tracking with relevant departments, we will soon publicly disclose a global reconnaissance system of the US government, which poses serious security threats to China's national security and world peace. We must be highly vigilant and tightly guard against this,' Xiao Xinguang, a member of the National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC), stated.
Why does it matter? The team warns that if the cyberattack damaged the earthquake monitoring system, it will lead to a greater loss of life and property. More dangerously, if the attackers tampered with the earthquake monitoring data, causing false alarms, it could lead to social panic, resulting in innocent casualties.
 Etiquetas calientes:
Ciberconflicto y guerra
Infraestructura crítica
Etiquetas calientes:
Ciberconflicto y guerra
Infraestructura crítica