






















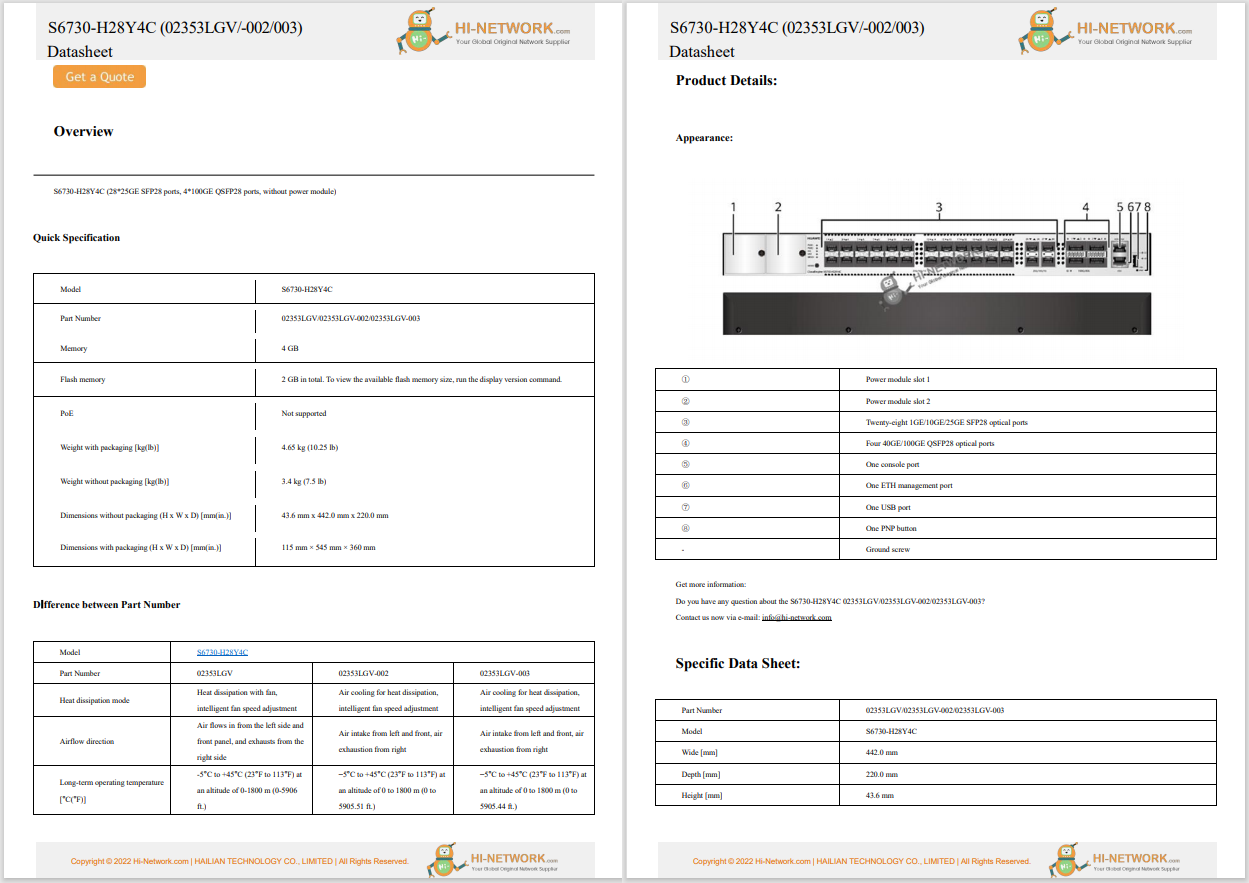


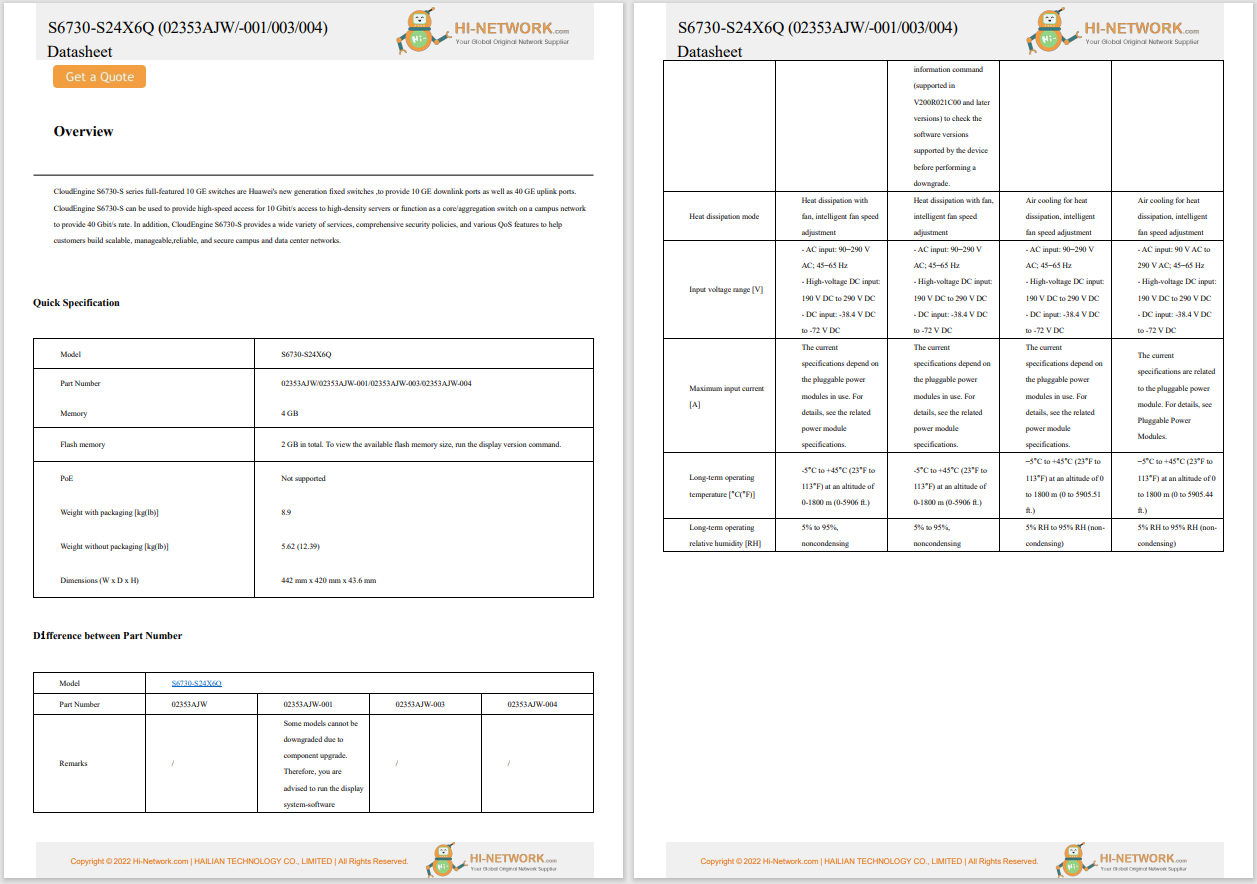
Critical infrastructure providers are increasingly implementing IoT systems to support, augment, or update their already networked operational technology. Further, critical infrastructure is often managed and deployed over connected systems supported or used by mobile professionals. At the same time, cyber threats to critical infrastructure remain of significant concern. Adversaries are constantly evolving their capabilities to attack and potentially disrupt critical infrastructure. As such, the need to build dynamic and resilient networks to support critical infrastructure is of the upmost importance.
One of the most effective ways to prevent or limit the damage of a cyber-attack on critical infrastructure is through security segmentation. However, traditional approaches to network segmentation that rely on static firewalls placed at choke points throughout a network have proven ineffective.
The answer to these shortcomings lies within Forrester's Zero Trust Model. The basis of the Zero Trust Model is to imagine how to implement security if all devices and networks were directly on the Internet. As such, critical infrastructure providers are unable to assume trust based on location, such as on a corporate Internet or within a physically secure facility or distributed location. The Zero Trust Model is especially relevant in that it provides an actionable technical framework for the protection of critical infrastructure. In order to securely communicate, devices that want to communicate on the network must be authenticated as does any individual using those devices and then a level of trust assigned. Communication must be constrained and protected via network isolation, or segmentation, and/or encryption. Policies that limit access to data and devices to only the minimum needed must be enforced. Visibility to actions of devices and individuals on the network must be achieved and security events be detected and appropriately actioned. Finally, all this must be orchestrated via a robust and automated platform.
Zero Trust Network Segmentation from Cisco
Cisco's SD-Access solution provides a holistic technology architecture that enables critical infrastructure providers to implement Zero Trust segmentation across their networks. A combination of Identity Services Engine (ISE) and the Duo authentication platform enables authentication of both users and devices as well as the ability to profile devices for policy enforcement. ISE also provides fabric based segmentation and dynamic threat control while Stealthwatch enables security visibility through Cisco NetFlow monitoring and analysis. All of this is managed and orchestrated via Cisco DNA Center, our control center for Intent Based Networking. Cisco can also extend comprehensive visibility, segmentation, and control into the data center via Cisco Tetration, ACI, and Firepower technologies enabling a complete approach to security segmentation for critical infrastructure providers.
However, Zero Trust segmentation for critical infrastructure requires more than just implementing point solutions, it truly is a transformational shift in how network and security is managed. As such, most organizations require assistance in building a strategy, architecture, and plan as well as expert assistance in implementation to build a Zero Trust network. Cisco's Security Segmentation Service provides a starting point to define the end state architecture and Zero Trust segmentation plan.
Our Segmentation Service starts by helping organizations determine their security and networking intent by examining what they need to protect, including core critical infrastructure and operational processes, how their organization functions, their critical applications and dependencies, and their applicable security and compliance requirements.
This is then used to build a Zero Trust Security Segmentation architecture. We start by defining a set of enclaves. Enclaves are a group of systems or devices that have a business affinity, are assigned the same level of trustworthiness, and have the same security policies applied. A set of controls are then defined for each enclave. Controls are technology solutions used to implement the Zero Trust Model. They include technologies that work together to provide for identity, policy enforcement, isolation, visibility and availability. It is through these controls that the Zero Trust segmentation model is realized. In parallel, we collect and analyze network traffic through StealthWatch in order to model real network traffic, both validating enclave definition as well as determining the necessary trusts between each enclave. Finally, we recommend an actionable roadmap for implementation that takes into account the necessary technology and operational maturity of the organization. This roadmap provides the necessary plan to implement Zero Trust segmentation. Implementation can be performed by the customer, Cisco, a partner, or an appropriate mix.
The Bottom Line
Critical infrastructure providers must protect their network in the face of an ever evolving threat landscape. With newer IoT and legacy operational technology increasingly being network attached, a Zero Trust approach to security segmentation provides a viable solution to enable secure and resilience operations. Through our comprehensive architecture and automation technologies as well as advisory planning and technology implementation services, Cisco is well positioned to help Critical Infrastructure Providers plan and implement a zero trust segmentation strategy.
 Etiquetas calientes:
#CiscoDNA
Cisco DNA
Zero Trust
Critical Infrastructure Security
Security Segmentation Service
Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience Month
Etiquetas calientes:
#CiscoDNA
Cisco DNA
Zero Trust
Critical Infrastructure Security
Security Segmentation Service
Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience Month