



























En hoy y#39;s fast-paced digital world, network performance and scalability are paramount for businesses striving to maintain a competitive edge. As organizations continue to grow, so does the complexity of their network infrastructure. To meet these demands, Cisco has introduced the Catalyst 1300 Series Switches, a powerful solution designed to optimize network efficiency and streamline management. One of the key features of the Cisco Catalyst 1300 Series is its stacking capability. This article delves into the concept of Cisco C1300 stacking, exploring its benefits, configuration, and best practices for implementation.
Cisco C1300 stacking refers to the ability to interconnect multiple Cisco Catalyst 1300 Series Switches to function as a single, unified system. This feature allows network administrators to manage multiple switches as if they were one, simplifying configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting. Stacking is a crucial feature for businesses that require scalability, high availability, and ease of management in their network infrastructure.
Cisco C1300 stacking offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive option for organizations looking to optimize their network operations:
When switches are stacked, they can be managed through a single IP address. This centralized management approach reduces the complexity of network administration by allowing changes to be made across all switches in the stack simultaneously. This simplifies tasks such as software upgrades, configuration changes, and monitoring, saving time and reducing the likelihood of configuration errors.
As businesses grow, so do their networking needs. Cisco C1300 stacking provides the flexibility to add additional switches to the stack as needed, without the need to reconfigure the entire network. This modular approach allows for seamless expansion and ensures that the network can scale with the business.
Network downtime can have significant financial and operational impacts on a business. Cisco C1300 stacking enhances network resilience by providing redundancy. If one switch in the stack fails, the remaining switches continue to operate without disruption. This ensures that critical network services remain available even in the event of hardware failure.
Stacked switches share a common backplane, allowing for high-speed data transfer between switches. This reduces latency and improves overall network performance. Additionally, traffic is automatically load-balanced across the stack, optimizing resource utilization and ensuring efficient data flow.
Understanding the architecture of Cisco C1300 stacking is essential for effective deployment. The Cisco Catalyst 1300 Series Switches support a ring topology, where each switch in the stack is connected to its neighbors. This creates a redundant path for data, ensuring continuous operation even if one connection fails.
The stack consists of a master switch and member switches. The master switch is responsible for managing the entire stack, including configuration, routing, and switch management. If the master switch fails, another switch in the stack automatically takes over as the master, ensuring uninterrupted network operation.
Configuring Cisco C1300 stacking involves several steps, including physical setup, software configuration, and verification. Below is a step-by-step guide to configuring a Cisco C1300 stack:
Connect Stacking Cables: Begin by connecting the stacking cables between the switches. Each switch should be connected to its neighbor, forming a ring topology.
Power on the Switches: Once the cables are connected, power on the switches. The switches will automatically detect the stacking cables and begin the initialization process.
Access the Master Switch: Log in to the master switch via the console or through SSH.
Assign Priority Values: The switch with the highest priority value becomes the master. Configure the priority using the following command:
switch 1 priority 15
Verify Stack Membership: Use the following command to verify that all switches are detected and part of the stack:
show switch
Configure Stack Interfaces: Configure the stack ports on each switch to ensure proper communication within the stack:
interface range g1/0/1-2
stack port enable
Check Stack Status: After configuration, verify the stack status using the command:
show switch detail
This will display the current stack members, their roles, and status.
Test Redundancy: To ensure redundancy, test the stack by powering off the master switch and observing the failover process.
To maximize the benefits of Cisco C1300 stacking, consider the following best practices:
Ensure that stacking cables are properly connected and secured to prevent accidental disconnection. Use cable ties and labels to organize cables and reduce the risk of human error during maintenance.
Keep the switch firmware up to date to ensure the latest features and security patches are applied. Cisco periodically releases updates that improve stack stability and performance.
Regularly monitor the health of the stack using Cisco’s network management tools. Look for signs of potential issues, such as high CPU utilization or interface errors, and address them promptly to avoid network disruptions.
When designing the network, plan for future growth by considering the maximum number of switches that can be stacked. Ensure that the power supply and cooling system can accommodate additional switches.
To further enhance stack resiliency, use redundant power supplies. This ensures that the stack remains operational even if a power supply unit fails.
While Cisco C1300 stacking is a robust solution, it may present certain challenges. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
Stack partitioning occurs when the stack loses connectivity between switches, leading to the formation of multiple, isolated stacks. This can be caused by a faulty stacking cable or port. To resolve this, check the physical connections and replace any damaged cables.
If the master switch fails and the stack does not automatically elect a new master, ensure that the priority values are correctly configured. Additionally, check the stack ports for errors and ensure that all member switches are functioning properly.
In some cases, switches with different firmware versions may fail to join the stack. Ensure that all switches are running the same firmware version before attempting to stack them.
Cisco C1300 stacking is a powerful feature that enables businesses to optimize their network infrastructure by simplifying management, enhancing scalability, and improving redundancy. By understanding the architecture, configuration, and best practices of Cisco C1300 stacking, network administrators can deploy a reliable and efficient network that meets the demands of today’s dynamic business environment.
Whether you are expanding an existing network or building a new one, the Cisco Catalyst 1300 Series Switches, with their stacking capabilities, provide the flexibility and performance needed to ensure seamless operations. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can confidently implement Cisco C1300 stacking and take full advantage of its benefits.
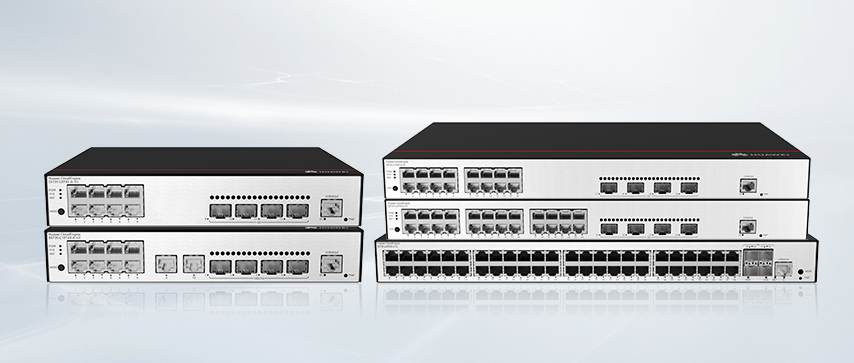
Cisco Catalyst 1300 Series Switches
For Cisco product list and quote, please visit: https://www.hi-network.com/categories/cisco or contact us at www.hi-network.com (Email: [email protected] (en inglés))
 Etiquetas calientes:
CISCO Switches
Etiquetas calientes:
CISCO Switches