















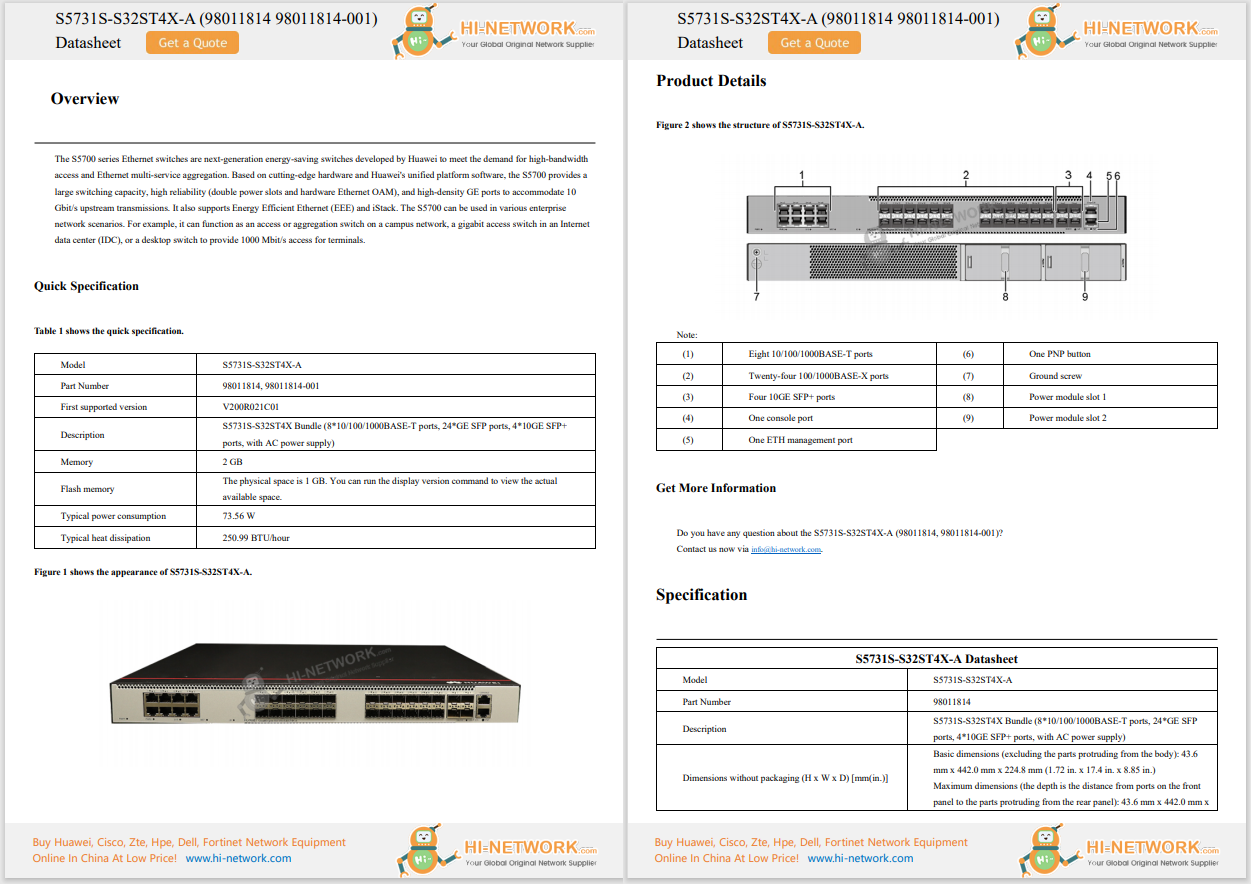










Even though the zero-trust security model has been around for more than a decade, it has received more attention because today's networks are more distributed and need to be able to support a hybrid work-from-anywhere workforce.
With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic and the sudden need to support remote employees, it quickly became apparent that traditional VPNs were not up to the task and the best approach for managing and securing users with no permanent location was to initiate a zero-trust strategy. With zero trust, anything or anyone trying to connect to the network is assumed to be a potential threat. And every user must be verified before permission to access resources is granted.
In April, Fortinet commissioned a survey of 570 IT and security leaders from 31 different countries, covering nearly all industries, including the public sector. The resulting 2023 State of Zero Trust Report provides insight into the progress IT teams are making in implementing their zero-trust strategies. It also highlights some of the challenges teams have faced in their efforts to secure rapidly changing and expanding network environments.
The good news is that since the last survey in 2021, the number of respondents reporting having deployed zero-trust solutions has increased substantially. The solutions that have been implemented include secure web gateways (SWGs) at 75%, cloud access security brokers (CASB) at 72%, network access control (NAC) at 70%, zero-trust network access (ZTNA) at 67%, next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) at 63%, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) with 62%.

Although the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) was at only 52%, it has increased substantially since 2021 when it was at 23%. MFA is an integral part of any zero-trust strategy because it's critical for preventing unauthorized access to applications and other resources.
The survey revealed that organizations are facing some serious challenges in implementing their zero-trust strategies. The first clue is that even though organizations have more zero-trust products deployed now, the implementation stats dropped. In 2021, 40% of respondents indicated that their zero-trust strategy was fully implemented, but in 2023, only 28% reported having a complete zero-trust solution in place. And the number of respondents now reporting being in the process of implementation is 66%, up from 54% in the previous survey.

These numbers indicate that perhaps making zero trust work was a little more difficult than anticipated. It's possible that many organizations that believed they had fully implemented a zero-trust solution are now rethinking that assessment. Some challenges probably didn't become obvious until a number of solutions were in place. Getting isolated point solutions to work together is notoriously difficult and troubleshooting workarounds can consume significant IT resources.

As far as the specific problems they faced, nearly a third (31%) of organizations reported latency issues as a significant challenge, and almost a quarter (22%) lament their over-reliance on traditional VPNs. It's clear that implementing a low-latency solution is critical to a successful ZTNA deployment.
Another interesting finding was that 16% of organizations and 24% of smaller companies complained that insufficient information is available to select a zero-trust solution. And 24% mentioned a lack of qualified vendors that are able to provide a complete solution, so they had to put something together on their own.
Many organizations have discovered that deploying solutions from multiple vendors has created new problems. Vendor and solution sprawl has led to unexpected security gaps and high operating costs, and according to the survey, 90% of organizations now rank vendor and solution consolidation as extremely or very important. Product interoperability is also deemed very or extremely important to 88% of respondents. It's clear that vendor and product consolidation and interoperability are crucially important to implementation.
For nearly half of the respondents (46%), the top concerns are that new exploitable security gaps and vulnerabilities have been created because solutions do not interoperate and cannot communicate. And 40% also report an inability to consistently apply and enforce policies. Related to these findings is the high cost of trying to keep a disjointed solution up and running, with 43% citing this problem as a top challenge. Other related challenges include poor user experience (39%), performance bottlenecks (36%), and increased management complexity (28%).

The survey indicated that even after the pandemic, many users are still working remotely, and 63% of organizations report having a hybrid workforce with users who move back and forth between their homes and workplace offices.

These findings reinforce those from the Fortinet 2023 Work from Anywhere Study, which revealed that 60% of companies in the study continue to accommodate employees working from home, and 55% of organizations are embracing a hybrid work strategy for their employees.
No matter where they're working, users need access to applications, which may be divided between cloud and on-premises. And 89% of respondents report SASE integration with their on-premises solutions is very or extremely important, which indicates the value of single-vendor (SASE) solutions that provide converged networking and security capabilities to all users and devices in distributed locations.
Today, most organizations still have a hybrid application and data strategy in place, and ZTNA needs to work no matter where applications and users are located. Respondents indicated that the top areas that a hybrid ZTNA strategy must cover include web applications (81%), on-premises users (76%), remote users (72%), on-premises applications (64%), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications (51%).
It's important to note that 72% of respondents also reported having issues with cloud-only ZTNA. Zero-trust should be everywhere. Organizations need a Universal ZTNA solution that supports applications in the cloud and on-premises, with consistent features and policies across deployments and a per-user licensing model so protections (and licenses) can move seamlessly as users move between their homes and on-premises offices.
Today, organizations need solutions that are designed to span multiple environments and can converge networking, security, and access into a single, integrated framework that enables proactive, integrated, and context-aware security that automatically adapts to where users are, what device they are using, and what resources they are accessing.
Learn more by downloading the full report and find out how to better secure access for remote users to applications anywhere with Fortinet Zero Trust Network Access.
 Etiquetas calientes:
Industry Trends
Zero Trust
ZTNA
Etiquetas calientes:
Industry Trends
Zero Trust
ZTNA