















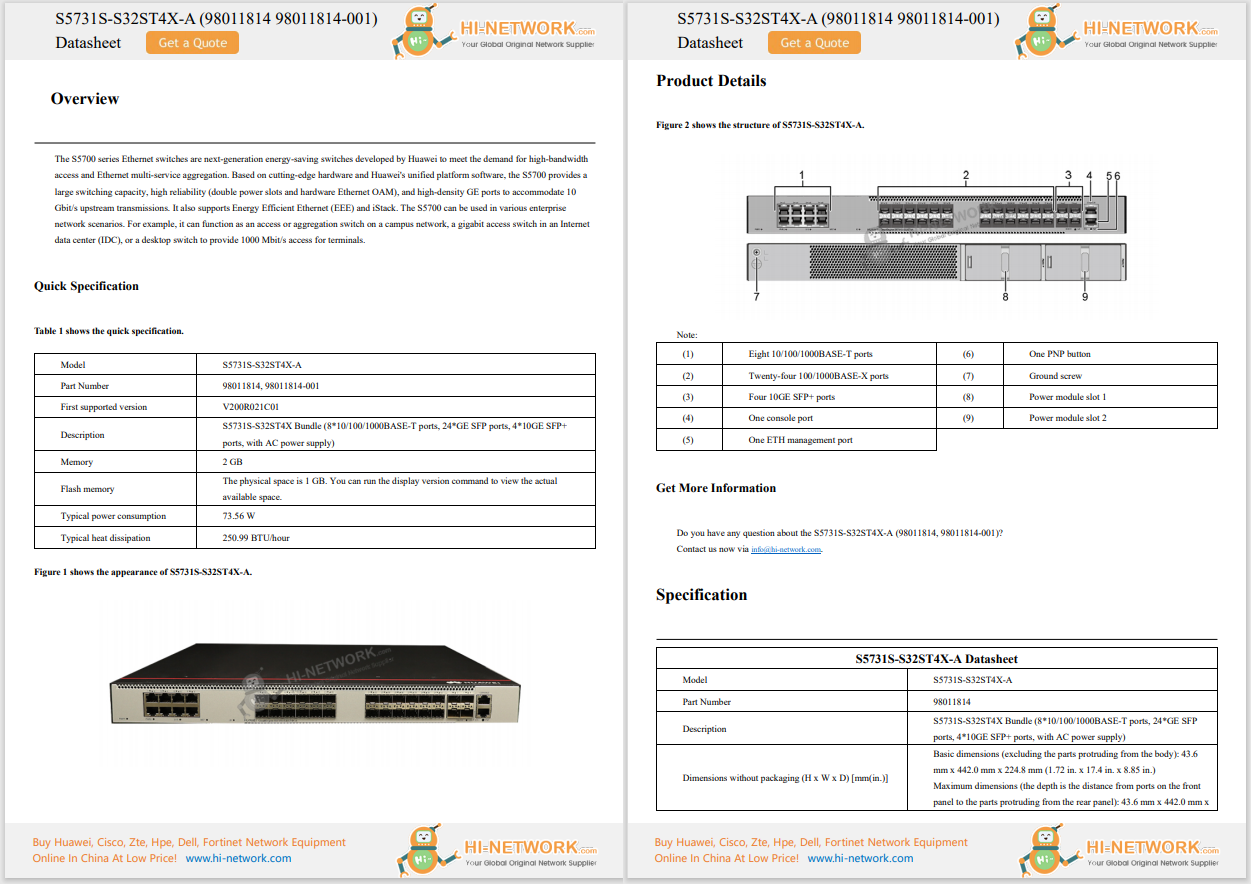










Google today unveiled Gemini, its most powerful generative AI (genAI) software model to date - and it comes in three different sizes so it can be used in everything from data centers to mobile devices.
Google has been developing the Gemini large language model (LLM) over the past eight months and recently gave a small group of companies access to an early version.
The conversational, genAI tool is by far Google's most powerful, according to the company, and it could be a serious challenger to other LLMs such as Meta's Llama 2 and OpenAI's GPT-4.
"This new era of models represents one of the biggest science and engineering efforts we've undertaken as a company," Google CEO Sundar Pichai wrote in a blog post.
The new LLM is capable of multiple methods of input, such as photos, audio, and video, or what's known as a multimodal model. The standard approach to creating multimodal models typically involved training separate components for different modalities and then stitching them together.
"These models can sometimes be good at performing certain tasks, like describing images, but struggle with more conceptual and complex reasoning," Pichai said. "We designed Gemini to be natively multimodal, pre-trained from the start on different modalities. Then we fine-tuned it with additional multimodal data to further refine its effectiveness."
Gemini 1.0 will come in three different sizes:
 Google
GoogleIn conjunction with the launch, Google also introduced its most powerful ASIC chip - the Cloud TPU v5p - specifically designed to handle the massive processing demands of AI. The new chip can train LLMs 2.8 times faster than Google's previous TPU v4, the company said.
LLMs are the algorithmic platforms for generative AI chatbots, such as Bard and ChatGPT.
Earlier this year, Google announced the general availability of Cloud TPU v5e, which boasted 2.3 times the price performance over the previous generation TPU v4. While far faster, the TPU v5p also represents a price point three-and-a-half times that of v4.
Google's new Gemini LLM is immediately available in some of Google's core products. For example, the Bard chatbot is using a version of Gemini Pro for more advanced reasoning, planning, and understanding.
The Pixel 8 Pro is the first smartphone engineered for Gemini Nano, using it in features like Summarize in Recorder and Smart Reply in Gboard. "And we're already starting to experiment with Gemini in Search, where it's making our Search Generative Experience (SGE) faster," Google said. "Early next year, we'll bring Gemini Ultra to a new Bard Advanced experience. And in the coming months, Gemini will power features in more of our products and services like Ads, Chrome and Duet AI."
Android developers who want to build Gemini-powered apps for a mobile device can now sign up for an early preview of Gemini Nano via Android AICore.
Starting Dec. 13, developers and enterprise customers will be able to access Gemini Pro via the Gemini API in Vertex AI or Google AI Studio, the company's free web-based developer tool. After more refinements to Gemini Ultra, such as extensive trust and safety checks, Google said it would be available to select groups first before it's available to developers and enterprise customers early in 2024.
Google's also announced a new AI accelerator, known as a tensor processing unit (TPU) and its AI Cloud Hypercomputer. The new TPU v5p is four times more scalable than TPU v4 in terms of total available FLOPs per AI pod.
 Google
GoogleLLMs require massive processing power because of the large dataset they ingest - a process called data pre-processing, organizing or sometimes labeling - before anything can be done with it. Next, the LLM must learn how to interpret the data in order to generate the next word, image, or line of computer code user queries request.
LLMs may need to learn billions or even more than a trillion parameters during training.
In addition to the new processor, Google announced its "AI Hypercomputer" from Google Cloud, a supercomputer architecture that employs an integrated system of performance-optimized hardware, open software, machine-learning frameworks, and flexible consumption models.
Customers can use the AI Hypercomputer to boost efficiency and productivity across AI training, tuning, and serving, according to Google.
 Etiquetas calientes:
Inteligencia Artificial
Chatbots
Tecnología emergente
Procesamiento del lenguaje Natural
Etiquetas calientes:
Inteligencia Artificial
Chatbots
Tecnología emergente
Procesamiento del lenguaje Natural